UV rays and their effects
Source: World Health Organisation
There are three main types of UV radiation from the sun. The most dangerous UV-C rays are completely absorbed by the ozone layer. The remaining two types, UV-A and UV-B, each have a different effect on the human body.
UV-A (400 – 315 nanometers)
UV-A radiation does not cause sunburn. Because of this, it was previously discounted as a potential cause of skin cancer, but new research has proven the link between UV-A and skin cancer.
The long waves of UV-A radiation penetrate the skin more deeply into the lower layers, where they produce a deep tan. They damage the connective tissue in these layers, causing premature ageing, wrinkles and loss of skin tone.
UV-B (315 – 280 nanometers)
Most of the UV-B radiation that reaches the Earth’s atmosphere is intercepted by the ozone layer. However, depletion in this layer has led to an increase in UV-B rays reaching ground level.
The short waves of UV-B radiation penetrate the upper layers of the skin, damaging DNA and causing it to tan as an attempt to protect itself. A brown pigment (melanin) is formed by the melanocyte (pigment cell) located where the epidermis meets the dermis. This pigment is then transmitted to the keratinocytes that are found in the epidermis.
If the dose of UV-B is too strong, the skin is sunburnt and inflamed, turning red as an alarm signal issued by the skin cells. These same cells then initiate self-repair to fix the damage.
The more often and more intensively the skin is sunburnt, the more often this process occurs, increasing the risk of faulty repairs and mutations. In the long term, this can lead to modification of the genetic material, chronic skin damage, the preliminary stages of cancer and, eventually, to skin cancer itself.
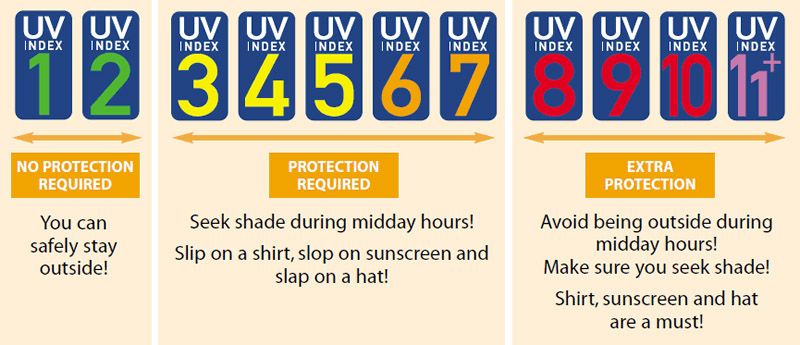
The UV Index
The UV Index is an international, scientific measure of the level of Ultraviolet radiation from the sun. It is used to describe the strength of the sun at a particular place and time. The index has a range of 1 to 11 - the higher the level, the greater the risk of skin damage.